Gastric Ballooning: A Beginner's Guide
1. Introduction: Understanding Gastric Ballooning
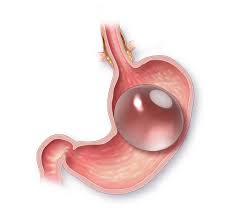
Gastric ballooning is a non-surgical procedure designed to assist individuals in their weight loss journey. It involves placing a silicone Gastric Balloon in Saudi Arabia into the stomach to reduce its capacity and promote a feeling of fullness. This temporary treatment helps control portion sizes, leading to a decrease in calorie intake and subsequent weight loss.
2. How Gastric Ballooning Works
During a gastric ballooning procedure, a deflated silicone balloon is inserted into the stomach through the mouth and esophagus. Once in place, the balloon is filled with a sterile saline solution, expanding its size. This process typically takes around 20 to 30 minutes and is performed under mild sedation.
The inflated balloon occupies space in the stomach, creating a sense of fullness even when consuming smaller amounts of food. As a result, individuals feel satisfied with smaller portions, leading to reduced calorie intake and gradual weight loss.
3. The Benefits of Gastric Ballooning
Gastric ballooning offers several benefits for individuals struggling with obesity or those who want to kick-start their weight loss journey. Some key advantages include:
a. Non-surgical Procedure
Unlike other weight loss surgeries, gastric ballooning is a non-surgical and reversible procedure. It does not involve any incisions, making it a less invasive option for those seeking to lose weight.
b. Short Procedure and Recovery Time
Gastric ballooning typically takes around 20 to 30 minutes to complete, and most individuals can resume their normal activities within a day or two after the procedure.
c. Temporary Treatment
The balloon remains in the stomach for a specific period, usually around six months. After that, it is deflated and removed, allowing individuals to resume their regular eating habits.
d. Weight Loss Results
Clinical studies have shown that gastric ballooning can result in significant weight loss. On average, individuals may lose 10-15% of their excess body weight during the treatment period.
4. Is Gastric Ballooning Right for You?
Gastric ballooning may be a suitable option for individuals who:
Have a body mass index (BMI) between 30 and 40.
Are committed to making lifestyle changes to support their weight loss journey.
Have not had success with conventional weight loss methods.
Do not want or qualify for invasive weight loss surgeries.
It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional experienced in weight management to determine if gastric ballooning is the right choice for you.
5. The Gastric Ballooning Procedure
Before the procedure, you will undergo a comprehensive evaluation, including medical tests and consultations with a gastroenterologist. The procedure itself involves the following steps:
Preparing for the procedure, which may include fasting for a specific period.
Administering mild sedation to ensure your comfort during the procedure.
Inserting the deflated silicone balloon through the mouth and esophagus into the stomach.
Inflating the balloon with a sterile saline solution.
Verifying the correct positioning of the balloon using imaging techniques.
Ensuring the balloon is securely sealed.
Removing the endoscope, completing the procedure.
6. Recovery and Aftercare
After the gastric ballooning procedure, you may experience some discomfort, nausea, or a feeling of fullness. These effects are temporary and typically subside within a few days. To support your recovery and maximize the benefits of gastric ballooning, follow your healthcare provider's instructions, which may include:
Adopting a specific diet plan tailored to your needs.
Incorporating regular exercise into your routine.
Attending follow-up appointments for monitoring and adjustments.
Seeking guidance from a nutritionist or dietitian.
7. Potential Risks and Complications
While gastric ballooning is generally considered safe, there are potential risks and complications associated with the procedure. These may include:
Nausea, vomiting, or abdominal discomfort in the first few days.
Balloon deflation or leakage, which may require removal or replacement.
Acid reflux or heartburn.
Infection or damage to the esophagus or stomach lining (rare).
It is crucial to discuss these risks with your healthcare provider and address any concerns before undergoing the procedure.


Comments
Post a Comment